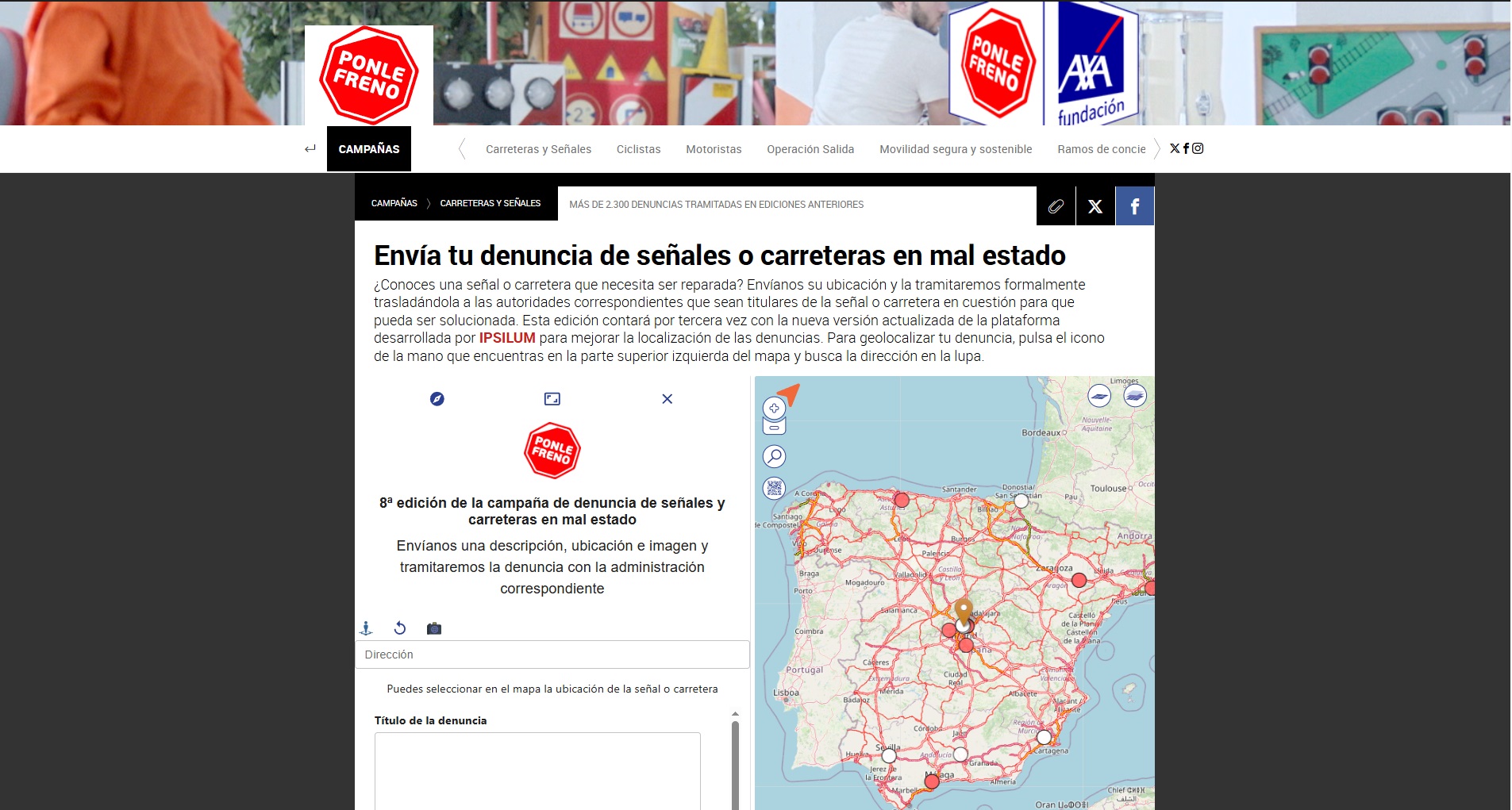
Road Safety Starts with You: Report Issues in Real Time with Ipsilum and Ponle Freno
With the application we have developed, any citizen can easily report a problem detected on roads or public spaces—whether it’s a pothole, a damaged sign, or a dangerous obstacle. The process is simple: just open the map on your phone, mark the exact location of the issue, and submit your report.